This vignette presupposes basic familiarity with the chef package, specifically the endpoint specifications and the data_prepare steps
Statistical method types in chef and chefStats
The chef framework categorizes statistical functions into three main categories depending on how they operate over stratification levels and treatment levels. Operations can either be done once per stratification level or treatment level, or they can operate across levels.
Figure 1 below shows a typical table from a safety analysis and color codes each result based on the function type that creates it:
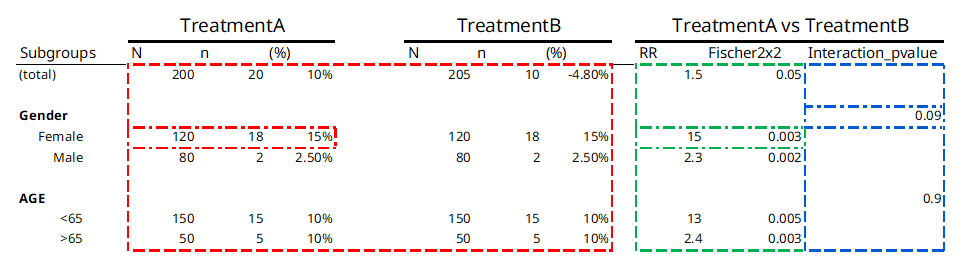
Figure 1
Table 1 below provides a description of each of the three
function types, color coded to the outputs they produce in table 1
above:
| Name | Description | Example function | Example application |
|---|---|---|---|
| stat_by_strata_and_trt | For each strata type (e.g. SEX, AGEGR, etc): one output per unique combination of strata level and treatment level |
n_subj() - Counts number of subjects in each stratification
level and treatment level
|
What is the total number of Females in TreatmentA |
| stat_by_strata_across_trt | For each strata type (e.g. SEX, AGEGR, etc): one output per strata level, across treatment levels |
RR() - Calculates the relative risk for the outcome/event
within a stratification level
|
What is the relative risk of having the outcome for females in Treatment A as compared to females in Treatment B |
| stat_across_strata_across_trt | One output per strata type (e.g. SEX, AGEGR, etc), across treatment levels |
p_val_interaction() - Test of interaction effect for
stratification level
|
Is the risk of having the outcome different across the strata of SEX |
The function type also determines when the function is applied. In
our example from figure 1, a
stat_by_strata_by_trt function will be
called once for each combination of stratification level and treatment
level, as well as once for TOTALS for each treatment level:
- SEX == “MALE” & TRT == “TreatmentA”
- SEX == “FEMALE” & TRT == “TreatmentA”
- SEX == “MALE” & TRT == “TreatmentB”
- SEX == “FEMALE” & TRT == “TreatmentB”
- AGE == “<65” & TRT == “TreatmentA”
- AGE == “>=65” & TRT == “TreatmentA”
- AGE == “<65” & TRT == “TreatmentB”
- AGE == “>=65” & TRT == “TreatmentB”
- TOTAL_ == “total” & TRT == “TreatmentA”
- TOTAL_ == “total” & TRT == “TreatmentB”
Whereas a stat_across_strata_across_trt will only be
called once per stratification “group”, i.e.:
- strata_var == “SEX”
- strata_var == “AGE”
